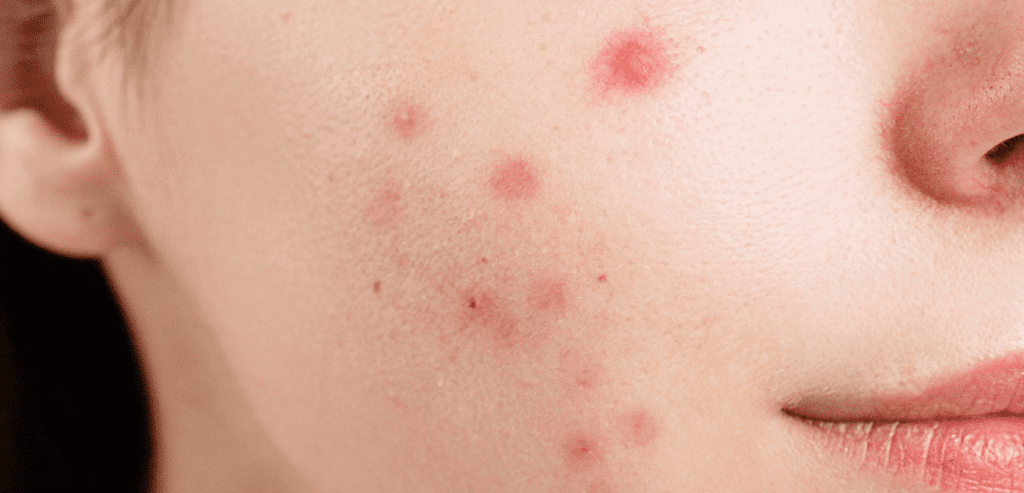
Thsi article is about Fungal Acne Causes Symptoms and Treatment Options. You are going to get detailed information about Fungal acne and how you can take care of it or help someone in need.
Fungal acne is not actually acne but is usually comfused with acne brcause it looks like acne and is now bearing the name “fungal acne.” Fungal acne, also called Pityrosporum folliculitis, is a common acne-like rash caused by an overgrowth of fungus in the pores of the skin.
What is fungal acne and what does fungal acne look like?
Contents
What causes fungal acne? to know that you must understand what causes a fungal infection in the first place.
What are fungal infections
A fungal infection is a condition that occurs when fungi invade and colonize host tissue. A wide variety of such infections occur in humans, other animals and plants.
The most common fungal infection in humans is athlete’s foot (tinea pedis), which affects between 10% and 20% of the population at any given time. Other common mycoses include ringworm (tinea corporis), candidiasis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, cryptococcosis and paracoccidioidomycosis.
Many types of fungus can cause infections in humans. The three main categories are dermatophytes (skin infections), yeasts (candidiasis) and molds (other forms). Certain species of non-pathogenic fungi can also infect humans or cause disease in other plant hosts; these include some molds (e.g., species of Aspergillus) and yeasts (e.g., Candida albicans).
Fungal infections are common in humans and animals. These fungal infections are caused by a fungus that enters the body through small cuts or abrasions in the skin, or through the mouth when eating contaminated food. The fungus spreads throughout the body and begins to multiply. Infected cells can die, and can cause tissue damage, which is what causes symptoms.
Signals of fungal acne infection
The signs of a fungal infection include fever, chills, muscle aches and pains, fatigue, weight loss and joint pain. If you suspect you have a fungal infection you should see your doctor for diagnosis and treatment options. But fungal acne infections, you might not get these symptoms as they ust initially start as bumps that look very similar to each other, having a red bumps and very itchy
Fungal infections are caused by fungi, which are single-celled organisms that live in soil and on plants. There are thousands of species of fungi. Some cause very minor infections, such as athlete’s foot. Others can cause life-threatening infections such as pneumonia or meningitis.
The fungus that causes Fungal acne is called pityrosporum. It’s a normal inhabitant of the skin, but for reasons not well understood it can sometimes become overgrown, resulting in the breakouts we call acne.
Fungal acne is usually limited to the upper part of your body, usually on your back and chest. This is because this is where hair follicles tend to be more exposed to air and less likely to be exposed to antifungal creams and shampoos.
Fungal acne usually appears as pimples or bumps on the upper surface of your skin which contain a white head (papule) with redness around it (erythema). The bumps are generally quite small, but they can get bigger if you squeeze them. Fungal acne can also appear as dandruff-like scales on the shoulders and back (sometimes even the face).
Fungal acne looks red and can hurt when you touch it. The spots are small and similar to pimples, but unlike pimples, Fungal acne does not come from blocked pores. It is not caused by dirt or oil and can be found anywhere on the body.
Treatment for Fungal acne is the same as for pimples, but since this type of acne is uncommon in most people, it may take some time to find a treatment that works. Many doctors suggest using a topical cortisone cream first to reduce the swelling and redness. If this doesn’t work, they often prescribe antibiotics to fight bacteria or isotretinoin to decrease sebum production. Fungal acne is also commonly treated with chemical peels and laser therapy.
Fungal acne causes and infections
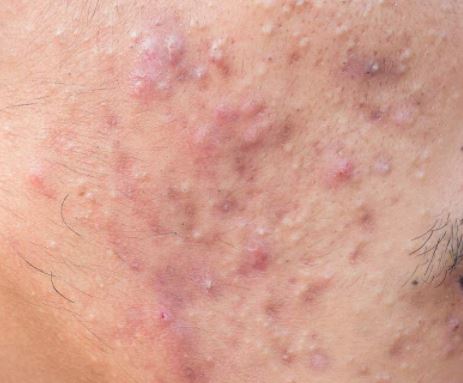
So what causes fungal acne?
Fungal acne is caused by a fungus, which is why it’s sometimes referred to as a “fungal infection.” But the fungus that causes it isn’t a pathogen — it doesn’t make you sick. The fungus thrives on the oil secreted by your sebaceous glands and dead skin cells. The problem is that this kind of fungus, known as “malassezia,” also feeds on the dead skin cells that slough off from your face.
Fungal acne usually occurs during hot, humid weather. The reason why it occurrs during hot, humid weather is because the fungi grows best in moist areas. Fungi that can cause this condition include Candida albicans and Malassezia furfur.
Fungal acne are a fungus infection of the skin. Fungal acne occur when a fungus infects the hair follicles or pores in the skin. The fungal infection of the skin is called tinea corporis and it is most common in teens and young adults.
Fungal acne are often misdiagnosed because the symptoms are identical to other skin conditions. When looking for fungal acne causes, it’s important to have a doctor examine the affected area. Some fungal acne can be treated with over-the-counter medications, however, severe cases may require prescription treatments.
One cause of fungal acne is wearing synthetic or tight clothing. Synthetic materials trap the moisture that causes the fungal acne to form on the skin. Tight clothing restricts blood flow which causes the skin to be deprived of oxygen and nutrients. Sweat also builds up in these areas and can cause fungal acne.
Fungal acne is a skin condition that is caused by the overgrowth of a fungus. The fungus that causes it is called Pityrosporum ovale. This fungus is commonly found on the skin of healthy people, but in certain circumstances it causes an outbreak of skin spots and pimples. Fungal acne tends to be more common in people who spend lots of time in hot, humid conditions or who sweat a lot.
Fungal acne usually appears as small, red bumps on the chest and back. Over time, these bumps may develop into larger pimples or pus-filled cysts that can cause pain and discomfort. In some cases, the cysts become infected with bacteria and may drain pus onto the skin.
Some ways that you can get fungal acne with makeup and preventivemeasures:
Wearing makeup that has become contaminated
Using unclean makeup applicators such as brushes, sponges, or cotton balls
Using unclean makeup storage containers such as jars, palettes, or compacts
Using unclean makeup brushes apply makeup to your face every day. If you have fungal acne on your hands, wash them carefully before touching your face. Be especially careful if you’re using new makeup products that you’ve never used before. It’s a good idea to clean your brushes on a regular basis. Open up the brush bristles and run them under warm tap water for about 30 minutes each week.
Add a little mild soap and let the brush sit in the water for a few minutes to thoroughly clean the bristles. Rinse out the soap and let them air dry on a towel. You may also clean them in a washing machine using laundry detergent on a gentle cycle. And throw away any makeup applicators
Fungal acne is a skin condition that is caused by a fungus growing on the face. You can get fungal acne from someone who already has it. Fungal acne is not the same thing as pustules or pimples, although it looks similar to them.
Fungal acne vs fungal acne pustules
There are two kinds of fungal acne: skin infections and follicular infections.
Skin fungal acne is a result of the excess skin yeast infection. It is easier to treat than a fungal acne caused by the hair follicles or pores.
Fungal acne pustules, on the other hand, are caused by the excess growth of fungus in hair follicles and pores inside your skin. Such fungal acne is more difficult to treat than the fungal acne on your skin.
Even under normal conditions, the human body is host to many species of fungi. Unlike bacteria, most fungi survive best in cool, dark environments where they can grow slowly and spread slowly. Fungi are also more likely to live in moist areas because their cells are made up mostly of water and require a lot of moisture for proper functioning.
The ideal conditions for growing fungus include:
(1) low oxygen levels; (2) high moisture level; and (3) a temperature that is relatively warm but not hot enough to kill the fungus.
The perfect place for fungi to grow would be places that have all three conditions—low oxygen, high humidity, and warm temperature—all at once. Fungi love dark places with high moisture levels and low oxygen
**Fungal acne is basically like a pimple and it is caused by the same type of fungus that causes athlete’s foot. However, unlike an athlete’s foot infection, this fungus thrives in your pores. It usually grows in areas of the body where there are no hairs to block the pores such as the face, back, shoulders and most commonly on the chest.
Fungus acne symptoms
If you’re looking for signs that you may have contracted fungal acne, pay attention to red sores that are ring-shaped and either tiny or large in size. Also keep an eye out for blackheads or whiteheads that are deep within the skin that become inflamed and often the blemishes will be oily in appearance.
The most common species of fungus that causes skin infections is called Pityrosporum ovale, which can cause a wide range of problems.
Fungus acne symptoms include small, white or black bumps on the forehead, chin, chest and back. Some people mistake these bumps for pimples at first. However, unlike pimples, fungal acne does not contain pus and may spread to other areas of the body.
While they may be unsightly, large cysts are more commonly associated with Pityrosporum folliculitis than the smaller bumps.
The severity of fungal acne symptoms can vary from person to person and from one occurrence to another. The lesions can occasionally become infected by bacteria like staph or strep, causing them to swell even more and spread to surrounding areas of skin.
Fungus acne is a very common skin problem that has to be taken seriously.
How contagious is fungal acne?
Fungal acne is contagious. It can be passed from person to person by sharing personal items such as towels or clothing. It can also be passed from one part of your body to another by touching an infected area and then touching another area, such as your face.
It is not uncommon for people to ask dermatologists this question. It is harder to find the answer, though. Many doctors are reluctant to talk about their personal experiences, for reasons of privacy and professionalism.
What we do know comes from studying outbreaks of fungal acne in hospitals or nursing homes. These outbreaks have a classic pattern: they start when one person, who may or may not have had acne before, and who may or may not be contagious at that moment, picks up the fungus on their skin. That person passes it on to others in the same way a sneezer spreads a cold: by touching them, and coming into contact with their contaminated surfaces afterward. The fungus then spreads from person to person until everyone who can be infected has been.*
The situation seems similar for fungal acne in the wild. The original patient usually has some kind of physical contact with an object that gets passed on (such as a ball or a diaper). Sometimes the patient touches another person directly, by touching their hair or kissing them. Then that second patient touches something else and so on.*
This pattern makes it clear why people sometimes get infected without having anything to do with the original patient: because other people who were exposed were infectious before they got sick. By studying outbreaks
Fungal acne is more contagious than bacterial acne. Fungi live everywhere, and they can spread by contact. They can even spread in the dark, which is why you should never share towels with someone who has a fungal infection.
How to treat fungal acne?
Treating fungal acne means taking steps to reduce the amount of dead skin cells, while also reducing the amount of oil produced by your sebaceous glands. It is also good to have a very good skincare routine.
Here are some suggestions for how to treat fungal acne:
Exfoliate, exfoliate, exfoliate! Keeping your skin clean is one of the best ways to prevent breakouts. You can use chemical exfoliants or physical exfoliants, but whichever kind you choose, be sure to follow up with a good moisturizer.
Keep your hair off your face. Long hair can trap humidity against the skin and clog up pores, causing breakouts. If necessary (or just for fun), try out some of these cool new hairstyles to keep
Ways to treat fungal acne
Tips and ways to treat fungal acne. The following steps are important:
- Wear clothes that are not tight to the skin or made of wool.
- Do not share clothes, towels, bedding, or clothing with other people.
- Wash your face and hands using soap and water daily.
- Use mild, non-medicated soap on your face once a day to remove oil, dead skin cells, and makeup from your skin’s surface.
- Do not use lotions or creams on your face unless prescribed by your doctor. Lotions and creams may clog pores and worsen fungal acne.
- Do not touch or scratch your face or pop pimples because this can lead to infection and scarring of the skin.*
- Make sure you take all of the medicine prescribed by your doctor to help clear up the infection caused by fungal acne.*
- Wash towels and other linens in hot water regularly (at least every week). This will help prevent fungal acne from spreading to family members and loved ones.*
- Practice good hygiene, including keeping fingernails clean.*
- If you are having trouble clearing up a stubborn case of fungal acne that is
There are a number of ways to treat fungal acne, ranging from the very simple to the very complicated. The most simple way is to just stop picking at your pimples. If you pick at your pimples, you’ll encourage more inflammation and make them worse—so if you want them to go away and not come back, stop picking at them.
How to get rid of fungal acne on forehead and face.
There are many causes of fungal acne on forehead. One of the most important things that you must do is to control the oil production on your face. This can be done with the help of anti-acne face wash that cleanses your face without removing essential oils from it. Some antifungal face washes contain natural ingredients like tea tree oil and salicylic acid. These ingredients are very good in preventing skin breakouts as they cleanse pores deeply without harming the facial skin. Regular cleansing with anti-acne face wash helps to prevent fungal acne on forehead and other parts of your body.
If you see a white layer on the affected area, it is a good sign that fungus has been killed by the treatment. A red bump or boil like eruption may also form after some days of usage; this is also a good sign, as it indicates that healing has begun in the affected area. It may take about 2 weeks for these symptoms to show up. Make sure you keep using such products for about 4-6 weeks so that the fungus does not return soon again.
You can also apply some topical creams containing benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid to kill fungus and reduce inflammation and redness in the affected area. Another
Fungal acne on forehead is the most common type of fungal acne. It appears as red, white and black spots on your forehead that are actually tiny infected hair follicles. They can be very itchy, but they aren’t contagious.
You should also avoid using any harsh or abrasive cleansers, as this may further irritate the affected area of your skin, causing further breakouts.
You may want to consult with a dermatologist to identify the best cleanser for you. You can also visit http://www.fungalacneguide.com/best-fungal-acne-treatment/ for more information on treating fungal infection on forehead using salicylic acid and benzoyl peroxide.
There are a number of treatments for fungal acne on forehead, including over-the-counter anti-fungal creams and prescription pills. Of these, the most effective method is usually prescription medicine.
Home remedies of fungal acne
If you are suffering with an outbreak of fungus, there are some home remedies that may help you get rid of it. One is to use tea tree oil and olive oil. Tea tree oil is a natural antifungal and antibacterial agent, while olive oil helps fight inflammation and scarring. The two oils should be mixed together in equal amounts, and then applied to the affected area using a cotton ball or piece of clean gauze.
Nizoral for fungal acne
One of the best ways to treat fungal acne would be Nizoral and ketoconazole. It is an antifungal treatment that is effective in treating a variety of fungal infections on our body. Another best shampoo is Ketomac which contains ketoconazole, an anti-fungal agent.
It comes in two forms: a liquid concentrate that mixes with water and a shampoo. The proper form depends on the severity of fungal acne on your body.
Nizoral is used as both a shampoo and cream for external use. The cream is applied once or twice a day to the affected area. The main ingredient in Nizoral inhibits the growth of fungi by interfering with its cell membrane, causing it to disintegrate. This causes the dermatophytes to die off and helps restore healthy skin tissue and relieve the symptoms of the condition.”
How to use Nizoral to treat fungal acne
Nizoral is a drug for treating fungal infections in the body. It is sold over the counter for use as a shampoo for mild to moderate dandruff, but there are other uses. The drug is effective against a wide range of fungi, so if you want to know how to use Nizoral for fungal acne, you may wish to read on.
Localized infections can be treated by applying Nizoral directly to the skin at the site of infection. The most common way of doing this is by washing your face with the shampoo (although it may sting a little). However, the solution can also be applied directly to areas of affected skin using cotton wool or gauze.
Nizoral is also a prescription medicine (prescription strength) that is used to treat fungal infections of the skin. It is also used to treat seborrheic dermatitis. Nizoral can be purchased over the counter, and can sometimes be purchased in generic form.
Nizoral works by killing or inhibiting the growth of certain fungi. You should not use it on fungal infections that are not caused by fungi or on any other medical problems that may cause you concern.
Bacteria that live on the skin and cause acne are sensitive to nizoral. Nizoral is a drug often used to treat fungal infections, but it is also used as a treatment for mild to moderate acne. The way it works is not fully understood. Just follow the directions on its usage when you buy it over the counter of being prescribed by your dermatologist after consultation.
Comedones vs fungal acne
The fact is that the cause of closed comedones and the cause of fungal acne are the same thing. The only difference is that one is caused by a fungus (a bacteria-sized creature) and the other is caused by a fungus (a skin cell).
The two conditions are basically identical. Which means you can cure them in basically the same way.
It’s helpful to remember that your skin is constantly renewing itself. It’s not as simple as it sounds, but when skin cells die they fall off, and new cells replace them. The process is called desquamation, which comes from “desquamate,” an old word for a flake of dead skin. But you are constantly losing dead skin cells, and you are constantly making new ones.
That’s why it’s possible to get bumps on your face even if you keep it clean: dead skin cells are always falling off your face, so there’s always something for bacteria or other fungi to feed off. That process produces what we call closed comedones: clogged pores.*
Fungal acne works the same way: dead skin cells fall off your face and provide food for fungi, which grow inside the pore and make more dead skin cells grow faster than usual, which plug
People often ask about the difference between closed comedones and fungal acne. It’s hard to answer, because there isn’t much of a difference. They are both caused by the same fungus, and they are exactly the same thing when you look at them under the microscope.
Treatment is also very similar: you need to use an antifungal cream, like amorolfine or ketoconazole, and keep using it for several months. This means washing your face with an antifungal soap such as chlorhexidine gluconate or tea tree oil soap twice a day, and applying cream after washing, and not touching your face except while washing.
What are comedones and closed comedones?
Comedones are small, tender bumps that develop just under the surface of the skin. They are not painful and disappear without treatment in a few days.
Comedones can be open or closed. Open comedones have a hair follicle in the center. Closed comedones have no opening to allow for the flow of oil (sebum) and dead skin cells (keratin).
Closed comedones occur when pores get clogged by excess oil and skin cells. The excess keratin and sebum build up around the hair follicle and thicken to form a plug. As the plug becomes larger, it causes surrounding tissues to swell and form a bump under the skin’s surface.
The most common areas for closed comedones are between the eyebrows, on the cheeks, around the nose, on the chin, along the jaw line, on the upper lip and around hairline. If you suspect you have comedones, look for these common trouble spots. If you see bumps that develop under your skin and clear up in a few days, you may want to consult a dermatologist to determine if they are acne or something else.
Comedones are also known as blackheads and whiteheads. Closed comedones are deep-seated, hard bumps under the skin that may take months to surface.
Comedones occur when pores become clogged with sebum and dead skin cells. The blockage mixes with bacteria and the result is a blemish.
Closed comedones occur when the build up of dead skin cells and sebum creates a hard shell around the clog. This hard shell is called an “infundibular plug.”
Fungal acne vs bacterial acne
If you have acne, you may be wondering what the difference is between fungal acne and bacterial acne. I was wondering that myself, so I looked into it.
Bacterial acne is the most common type of acne. It is caused by one of several different strains of bacteria, including Propionibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Typically, inflammation results from an infection with these bacteria and results in pustules. Pimples are also caused by this type of bacteria.
Treatment for bacterial acne includes benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid to kill the bacteria and antibiotics to treat secondary infections. Antibiotics can also decrease redness and swelling if infected cysts develop.
Fungal acne is less common than bacterial acne, but still affects many people. It often affects the beard area or the groin where fungus thrives in warm, moist areas. The red, itchy bumps are referred to as pityriasis folliculorum or “ringworm of the skin”. The infection is caused by a fungus called malassezia furfur and can be treated with antifungal cream or oral medications such as ketoconazole.
So how do you tell fungal acne from bacterial
Fungal acne is a rare and treatable form of acne that causes small, red bumps on the face. These are often referred to as “pityriasis rosea” or “tinea versicolor” and caused by infection with the yeast-like fungus Malassezia furfur.
The fungi can sometimes be spread from other skin sites to the face, for example, by using hair care products containing oils or other ingredients that may increase the growth of fungal organisms. Fungal acne occurs more frequently in males than females and usually starts in adulthood. In general, fungal acne tends to occur in fair-skinned individuals with oily skin.
How to Prevent Fungal Acne Infections
Aside from common skin problems, fungus is also a potential cause of acne. If you are experiencing the symptoms of this condition, you should consider treating it with an oral or topical antifungal. If you are not sure whether your condition is fungal or not, you should consult a dermatologist to find the proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. It is always better to prevent acne than to treat it, so there are several ways you can prevent fungal acne.
The first step to getting rid of fungal acne is recognizing it. The best way to do this is to find out if you have any risk factors. Although fungal acne is a condition that can take weeks or months to clear up, if it is a severe case, you should seek medical care immediately. A good treatment for this skin disorder is to avoid the causes of this condition. The most common causes of this kind of acne are the same as those of other types.
If you’re concerned that you may have fungal acne, your first step is to avoid wearing tight clothes for several hours after your activity. You should also make sure to change after sweating. While it is true that you can avoid tight clothing, it’s important to change your clothes frequently. Tight clothes can encourage yeast growth on the skin. For severe cases, you should consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis. If you’ve tried everything to treat the condition, you should consider treating it with an antifungal.
While fungal acne is usually treated the same as regular acne, it is not easy to identify. Generally, you can simply treat this type of acne by using topical antibiotic creams. However, if you’re experiencing a serious breakout, you may need to use oral antifungals. For more serious outbreaks, you can use a special shampoo containing pyrithione zinc and selenium sulfide. You should apply this shampoo directly to the affected areas when you shower.
In addition to applying antifungal creams, you should also avoid shaving as this can cause yeast to enter the hair follicle. To avoid the infection from spreading, make sure you clean your skin with soap or a moisturizer. Moreover, you should stay away from oily lotions and fitness gears. The yeast feeds on excess oils on the skin, so they can cause a fungal breakout on your body.
If you have fungal acne, you can use topical antifungal creams to combat it. Oral antifungals are more effective in treating more persistent outbreaks. If you’re not able to use topical products, you can also use dandruff shampoos containing pyrithione zinc and selenium sulfide. These shampoos can be used as cleansers on the affected areas of the body during your showers.
Fungal acne can appear on the arms, the back, the chest, the scalp, and the face. The most common places to find this condition include the T-zone on the face, the chest, and the arms. It’s important to consult a dermatologist if you have fungal infections on any of these parts of the body. These products can help with the treatment of fungal acne, so they should be your top choice.
Fungal acne is contagious, but it’s not always contagious. If you have fungal acne on your arms or legs, you can use athlete’s foot cream or a dandruff shampoo. These creams have antifungal properties, and should be applied twice a day. In severe cases, oral antifungal medications may be necessary. In such cases, it’s best to consult a board-certified dermatologist.
How difficult is fungal acne to treat?
Fungal acne can be difficult to treat, but it is treatable. It will likely clear up within a few weeks. While it doesn’t have the characteristics of normal acne, it can be treated successfully. Fortunately, many fungal acne solutions don’t require prescriptions. And you’ll find a variety of effective solutions in pharmacies that you can purchase over-the-counter. The best options are often more expensive than the average drugstore, so it is essential to speak with a doctor before you make any changes to your treatment.
You should visit a dermatologist if you suspect you have fungal acne. These doctors can help you determine the cause of your condition and prescribe the appropriate treatment. It’s important to consult a board-certified dermatologist if you’re concerned about recurring fungal acne. They will prescribe a customized treatment plan for you based on your specific case. Once your physician has confirmed your condition, he or she will determine which of the two treatments is best for you.
I hope that this article has provided you with enough information on Fungal Acne Causes Symptoms and Treatment Options.
Dysport vs Botox – Which is More Effective for Reducing Wrinkles?
This article addresses the Dysport vs Botox debate. What is the difference between them when it comes to treating wrinkles and other skin conditions? The aging process has a way of creeping up on us. As we age, we start to notice fine lines and wrinkles that are more noticeable with time. We also start […]
How Much Does Microneedling and Chemical Peel Cost?
Whenever you want o have a procedure done, one of the first thing that comes to your mind is the cost or affordability. This article is about microneedling and chemical peels cost , and how they differ in treating different skin conditions. With so many treatment choices available today, it can be hard to choose […]
Fractional Laser Resurfacing | Entire New Way To a Younger Looking Skin
If you are looking to restore a youthful appearance to your skin, then laser fractional resurfacing may be the answer. In this post, we describe the different types of laser resurfacing and how they can help you achieve your desired results. This is a revolutionary new way to get younger looking skin. But when I […]
How to Build a Successful SkinCare Routine For Women And Men
This article is about how to build a successful skincare routine. Keeping yourself clean and looking fresh and beautiful can be accomplished by means of an effective and good skincare routine. The best way to achieve this is by making sure that the products that you buy for your skincare are suitable for your skin […]
